Datus Tutorial: A Complete Walkthrough for contextual data engineering¶
A step-by-step guide to understanding and practicing Contextual Data Engineering
This tutorial walks you through the full workflow of Datus-agent:
- Build the knowledge base (Metadata / Metrics / Reference SQL)
- Generate two subagents with tools and context
- Explore the data context with Datus-CLI
- Benchmark them to compare accuracy and performance
- Run multi-round evaluation to demonstrate the value of contextual data engineering
1. Prerequisites: Initialize Your Datus Agent¶
Before running the tutorial, initialize your Datus agent:
Since this tutorial involves metric generation, you also need to install the semantic layer adapter:
For detailed setup instructions, see the Quick Start Guide.
2. Run the Tutorial¶
Start the guided tutorial:
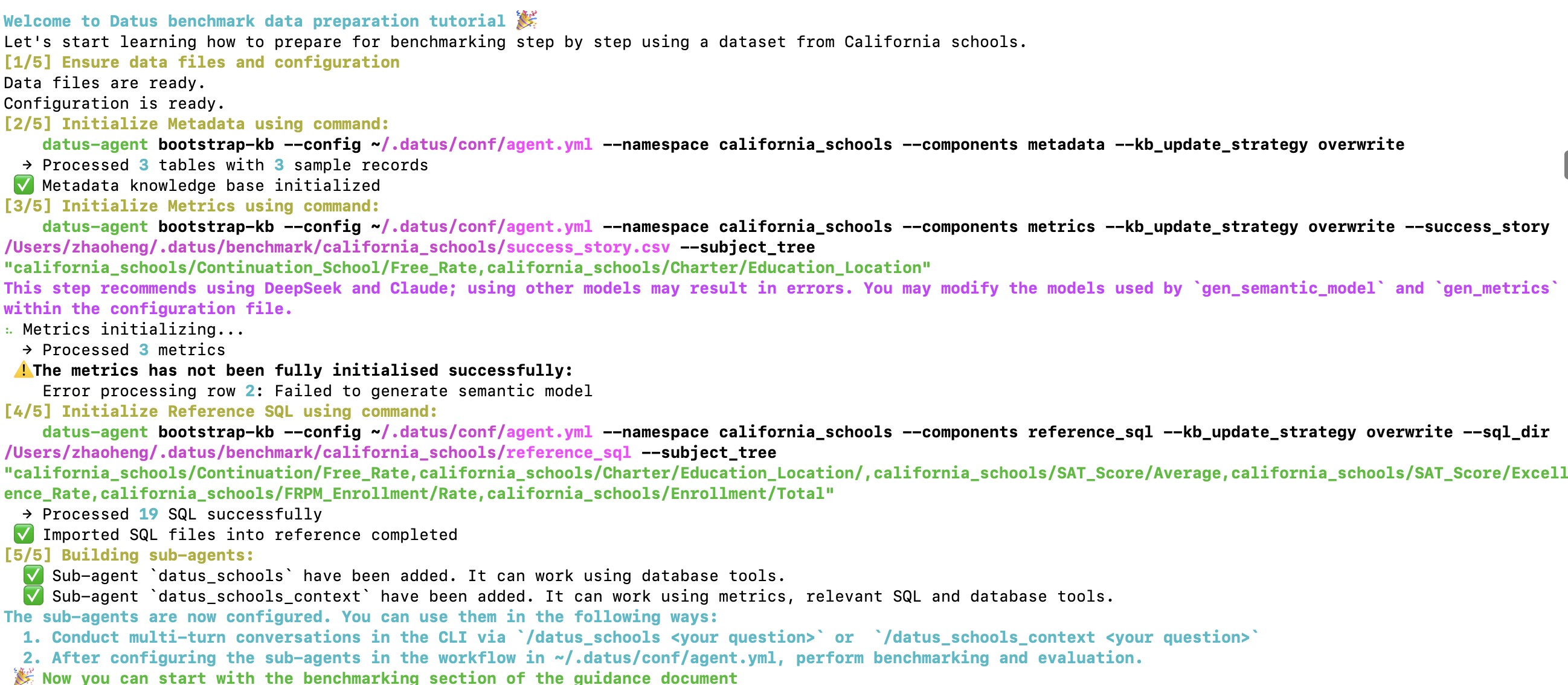
You will see a structured 5-step workflow. This will take approximately 10 minutes to initialize through multi-turn agent calls. You can watch Datus's execution process during the wait to understand how it works.
Step [⅕] Validate Data & Configuration¶
Welcome to Datus tutorial 🎉
Let's start learning how to prepare for benchmarking step by step using a dataset from California schools.
[1/5] Ensure data files and configuration
Data files are ready.
Configuration is ready.
The tutorial checks:
- Copies and validates the example dataset (california_schools)
- Verifies success_story.csv exists
- Confirms reference_sql/ directory is present
- Updates agent.yml with the configuration
Step [⅖] Initialize Metadata¶
[2/5] Initialize Metadata using command:
datus-agent bootstrap-kb \
--config ~/.datus/conf/agent.yml \
--namespace california_schools \
--components metadata \
--kb_update_strategy overwrite
Example output:
Datus will connect to the example dataset, extract table schemas and data samples, then store them into the knowledge base with vector index. Learn more about metadata management.
Step [⅗] Initialize Metrics¶
Metrics generation depends heavily on semantic modeling, so strong agentic models are preferred. (Recommended models: DeepSeek / Claude). For more details, see metrics documentation.
[3/5] Initialize Metrics using command:
datus-agent bootstrap-kb \
--config ~/.datus/conf/agent.yml \
--namespace california_schools \
--components metrics \
--kb_update_strategy overwrite \
--success_story ~/.datus/benchmark/california_schools/success_story.csv \
--subject_tree "california_schools/Continuation_School/Free_Rate,california_schools/Charter/Education_Location"
Understanding the parameters:
--success_story: A CSV file containing sample question & SQL pairs. The LLM will analyze these examples to extract and generate business metrics.--subject_tree: A pre-defined semantic layer classification structure (e.g.,california_schools/Continuation_School/Free_Rate). The LLM will organize generated metrics into appropriate leaf nodes within this subject tree.
Example output:
⠦ Metrics initializing...
→ Processed 3 metrics
⚠️ The metrics has not been fully initialised successfully:
Error processing row 2: Failed to generate semantic model
Note If metrics initialization fails, adjust the model configuration for
gen_semantic_modelandgen_metricsin agent.yml. These errors can be safely ignored if you don't have enough success story examples at the beginning.
Step [⅘] Initialize Reference SQL¶
For more information about reference SQL, see the reference SQL documentation.
datus-agent bootstrap-kb \
--config ~/.datus/conf/agent.yml \
--namespace california_schools \
--components reference_sql \
--kb_update_strategy overwrite \
--sql_dir ~/.datus/benchmark/california_schools/reference_sql \
--subject_tree "california_schools/Continuation/Free_Rate,california_schools/Charter/Education_Location/,california_schools/SAT_Score/Average,california_schools/SAT_Score/Excellence_Rate,california_schools/FRPM_Enrollment/Rate,california_schools/Enrollment/Total"
Understanding the parameters:
--sql_dir: Directory containing reference SQL files. Datus will parse, analyze, and segment these SQL files to build reusable SQL summaries.--subject_tree: A manually designed classification structure. The LLM will categorize and organize the SQL summaries into the appropriate subject tree nodes. It's recommended to design this classification structure manually for better organization.
Output:
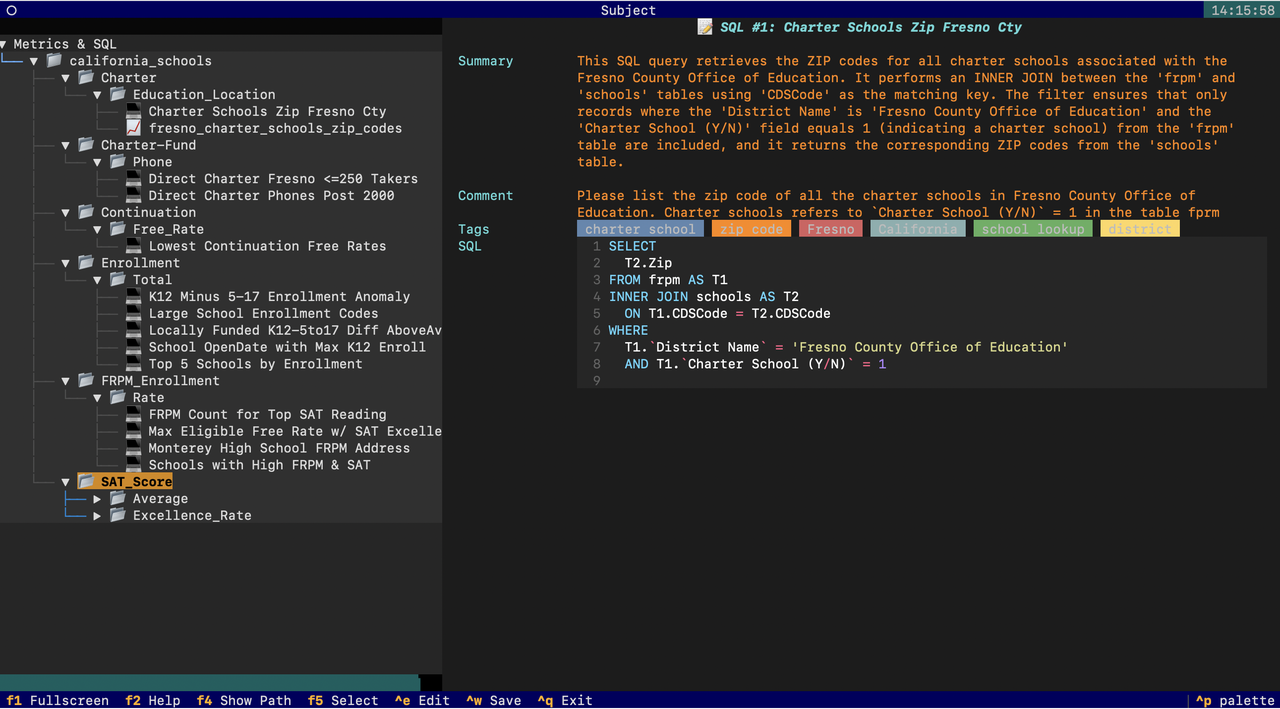
You can explore the metrics and reference SQL generated by Datus using Datus-CLI:
Step [5/5] Build Subagents¶
The tutorial automatically generates two subagents:
[5/5] Building sub-agents:
✅ Sub-agent `datus_schools` have been added. It can work using database tools.
✅ Sub-agent `datus_schools_context` have been added. It can work using metrics, relevant SQL and database tools.
Check the agent.yml configuration file to see the subagent definitions:
agentic_nodes:
datus_schools:
system_prompt: datus_schools
prompt_version: '1.0'
prompt_language: en
agent_description: ''
tools: db_tools, date_parsing_tools
mcp: ''
rules: []
datus_schools_context:
system_prompt: datus_schools_context
prompt_version: '1.0'
prompt_language: en
agent_description: ''
tools: context_search_tools, db_tools, date_parsing_tools
mcp: ''
rules: []
workflow:
datus_schools:
- datus_schools
- execute_sql
- output
datus_schools_context:
- datus_schools_context
- execute_sql
- output
Understanding the configuration:
agentic_nodes: Defines the two subagents with different capabilities
datus_schools: Baseline agent with onlydb_toolsanddate_parsing_toolsdatus_schools_context: Context-rich agent with additionalcontext_search_toolsthat can access metrics and reference SQL from the knowledge base
workflow: Defines the execution flow for each agent. These workflows are designed to output results to files, making it easy to evaluate and compare agent performance.
- Step 1: Subagent analyzes the question and generates SQL
- Step 2:
execute_sqlnode executes the generated SQL to produce the final result - Step 3:
outputnode formats and writes the results to local disk
The key difference is that datus_schools_context has access to context_search_tools, enabling it to leverage the metrics and reference SQL you built in previous steps.
You can now:
Or use the chatbot in Datus-Chat.
3. Benchmark and evaluation¶
This is the key part of the tutorial: comparing a non-context agent vs. a context-rich agent.
3.1 Evaluate datus_schools (baseline)¶
datus-agent benchmark --namespace california_schools --benchmark california_schools --workflow datus_schools
Save the results:
datus-agent eval --namespace california_schools --benchmark california_schools --output_file schools1.txt

3.2 Evaluate datus_schools_context (full context)¶
datus-agent benchmark --namespace california_schools --benchmark california_schools --workflow datus_schools_context
Save the results:
datus-agent eval --namespace california_schools --benchmark california_schools --output_file schools2.txt
Example evaluation output showing detailed metrics and performance analysis for both agents.
By comparing schools1.txt and schools2.txt, you can explicitly see how the context-rich agent improves SQL accuracy, reduces errors, and generates more semantically correct queries compared to the baseline agent.
4. Multi-round Benchmark: Demonstrate Context Evolution¶
This is the most powerful demonstration of contextual data engineering:
python -m datus.multi_round_benchmark \
--config ~/.datus/conf/agent.yml \
--namespace california_schools \
--benchmark california_schools \
--workflow datus_schools_context \
--max_round 4 \
--group_name context_tools
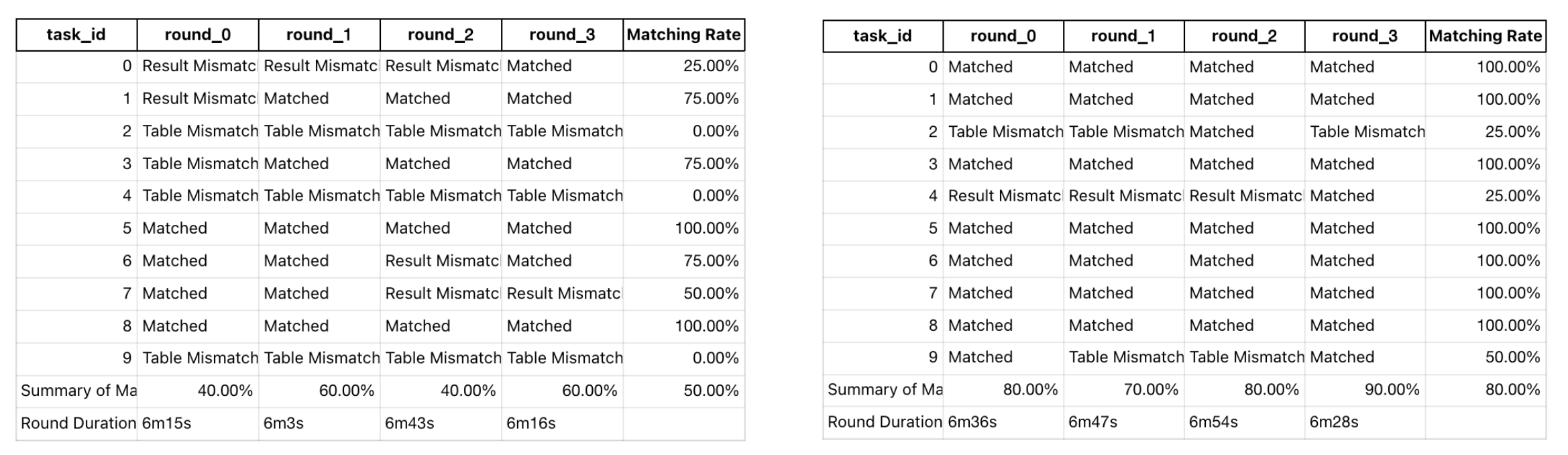
The left graph shows the benchmark result without data context tools (datus_schools), while the right graph shows the benchmark result with data context tools (datus_schools_context). Notice the significant improvement in accuracy when context is available.
5. Summary¶
By completing this tutorial, you have:
| Component | What You Achieved |
|---|---|
| Metadata bootstrap | Loaded schema, column descriptions, and physical structures |
| Metrics bootstrap | Created semantic models and business metrics |
| Reference SQL import | Captured real SQL patterns and joins |
| Subagent creation | Built domain-scoped, context-rich agents |
| Benchmarking | Measured SQL correctness and LLM reliability |
| Multi-round evaluation | Observed how context improves accuracy over time |
You now have:
- ✔ A fully usable domain subagent
- ✔ An evolvable knowledge base
- ✔ A repeatable benchmark and evaluation framework
- ✔ A real demonstration of contextual data engineering
Next Steps¶
- Explore Datus-CLI for interactive data exploration
- Learn about workflow orchestration for production use cases
- Discover database adapters for different data warehouses